Perl Basics and Biostatistics
Sensitivity and Specificity
In this lesson the student will learn how to:
- calculate sensitivity and specificity
- create subroutines in Perl
By the end of this lesson the student will be able to:
Write a script which calculates sensitivity
and specificity using subroutines.
Specificity - the fraction of those without the disease who get a negative
test result.
These concepts can be represented as:
TP TN
Sensitivity = ------- Specificity = -------
TP + FN TN + FP
TP - true positive
FP - false positive
TN - true negative
FN - false negative
These categories can be represented like this in a simple table:
| Disease
Present | Disease
Absent |
| Test Positive | TP | FP |
| Test Negative | FN | TN |
In general a test with high sensitivity can rule out a disorder with a
negative result since relatively few negative results will be false
negatives. A test with high specificity will rule in the disorder with a
positive result since relatively few positive tests are false positive.
A Perfect Test
In a perfect test there is a perfect correlation between those with the
disease and a positive test result and those who do not have the disease and
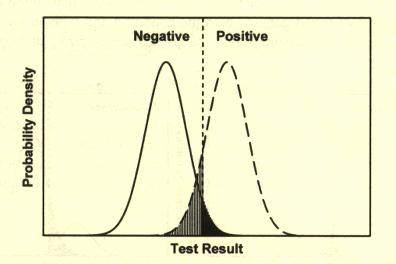
a negative test result. In a typical test there is a good deal of overlap
between these groups. A perfect test can be represented like this:
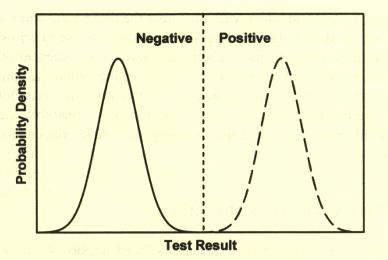
The dashed line represents the demarcation between positive and negative
test results. The experimenter sets this line and in the case of the perfect
test it is easy to decide where to place it. In the case of the typical
test, this decision is not so easy. Due to the overlap between the groups,
the placement of the line of demarcation has an impact on the diagnosis
rendered. Setting it further to the right increases the number of false
negatives (which means that more people with the disease may be considered
not to have the disease - this is not a good thing). Setting the line of
demarcation further to the left increase the number of false positives
(which means that more people without the disease will be told that they do
have the disease which could be psychologically traumatic for them, but
further testing should resolve this situation).

Subroutines in Perl
A subroutine is a separate body of code designed to perform a particular
task. Subroutines are called or invoked from the main body of your script.
The act of invoking a subroutine is called subroutine invocation. Here's a
quick example:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
$total = 0;
&getnumbers;
foreach $n (@numbers){
$total += $n;
}
print "Total: $total\n";
sub getnumbers{
print "Enter a list of numbers separated by spaces (no commas):\n";
$line = <STDIN>;
$line =~ s/^\s+|\s*\n$//g;
@numbers = split(/\s+/, $line);
}
exit;
NOTE: Don't worry about the s/ / /g construct or the split
function yet. You won't need them for the assignment below.
This program could have been written slightly differently like this:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
$total = 0;
@numbers = &getnumbers;
foreach $n (@numbers){
$total += $n;
}
print "Total: $total\n";
sub getnumbers{
print "Enter a list of numbers separated by spaces (no commas):\n";
$line = <STDIN>;
$line =~ s/^\s+|\s*\n$//g;
split(/\s+/, $line);
}
exit;
Here's another example for you:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
srand();
print "Random Number Tester.\n";
for($count = 1; $count <= 100; $count++){
$randnum[&intrand] += 1;
}
print "Totals for the digits 0 - 9:\n";
print "@randnum\n";
sub intrand{
$num = int(rand(10));
}
exit;
Here's another example which actually uses the return statement:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
$total = &get_total;
if($total eq "error"){
print "No input supplied\n";
}
else{
print "Total: $total\n";
}
sub get_total{
$value = 0;
print "Enter values: ";
$input = <STDIN>;
$input =~ s/^\s+|\s*\n$//g;
if($input eq ""){
return "error";
}
@vals = split(/\s+/, $input);
foreach $v (@vals){
$value += $v;
}
return $value;
}
exit;

ASSIGNMENT:
Write a script with the following subroutines:
- getTP() - takes input for true positive value
- getFP() - takes input for false postive value
- getTN() - takes input for true negative value
- getFN() - takes input for false negative value
- calcSENS() - calculates sensitivity and prints result
- calcSPEC() - calculates specificity and prints result

